Corn and Soybean Stand Assessment
- Corn and soybean stands should be assessed early in the season to help identify potential crop concerns.
- After seedlings emerge, stand counts and visual inspection of the plants can help identify issues caused by planting, insects, and/or diseases.
- Three common methods for taking stand counts are the 1/1000th acre method, the wheel method, and the hoop method.
Corn and soybean stands should be evaluated by counting plants that have a good chance of survival. Keep in mind that while corn plant populations are a critical component of yield, soybean plants are better able to compensate for low plant populations.
1/1000th AcreMethod
Count the number of plants in a length of row equal to 1/1000th of an acre based on row width(Table 1). Multiply the number of plants by 1,000to get plants per acre.Repeat the process in several locations in the field for an accurate estimate.
Wheel Method
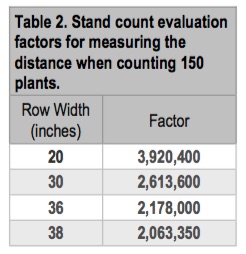
Count 150 plants and measure the distance from start to finish with a measuring wheel. Divide the number of feet traveled into the appropriate factor in Table2 to determine plant population. For example, if you walked 94 feet while counting 150 plants in 30-inch rows, the population is 2,613,600 ÷ 94 = 27,804 plants per acre. You may repeat the count several times and average the results.
Hoop Method
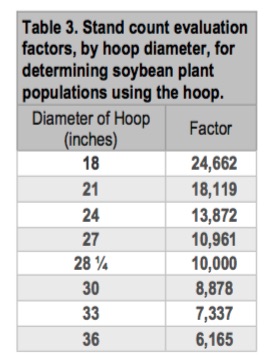
This method should be used for drilled soybeans.Measure the diameter of the hoop, toss it in the field, and count the number of plants inside the hoop. Do this in at least 5 locations in the field.Multiply the average number of plants by the appropriate factor listed in Table 3 to get the number of plants per acre. Notice that having a diameter of 28 1⁄4 inches allows you to simply multiply by 10,000 to obtain the number of plants per acre.This size of hoop can be made by cutting anhydrous tubing to 88 3⁄4 inches and joining it to form a circle.
If a crop stand is being assessed for potential replanting, several factors should be taken into consideration, including if the field is irrigated or dryland, plant population, plant spacing, and the date of potential replanting.
Got questions? Give us a call:
(701) 898-4466

